Cells are the smallest unit of life.
All living things are made of cells.
Most human cells, like most other animal cells, have the following parts:
- nucleus
- cytoplasm
- cell membrane
- mitochondria
- ribosomes
Plant cells also have:
-cell wall
-chloroplasts
-permanent vacuole
What do these structures do?
- Nucleus – controls the activities of the cell.
- Cytoplasm – where most of the chemical reactions take place.
- Cell membrane - controls the passage of substances in and out of the cell.
- Mitochondria - where most energy is released in respiration.
- Ribosomes - where protein synthesis occurs.
- Cell wall - strengthens plant cells.
- Chloroplasts - absorb light energy to make food in plant cells.
- Permanent vacuole - filled with cell sap in plant cells.
There are many similarities and differences between animal and plant cells.
Make sure you know these.
| Similarities | Differences |
| 1. Have a nucleus | 1. Plant cells have a cellulose cell wall |
| 2. Have a cytoplasm | 2. Plant cells have a vacuole containing cell sap |
| 3. Have a cell membrane | 3. Plant cells have chloroplast |
| 4. Contain mitochondria | 4. Many plant cells have a box-like shape whilst animal cell shape varies |
| 5. Contain ribosomes | 5. Plant cells have the nucleus to the side of the cell, animal cells have a nucleus in the middle |
Other facts:
The chemical reactions inside cells are controlled by enzymes.
Examples:
- Enzymes for respiration are in the mitochondria.
- Enzymes for photosynthesis are in the chloroplasts.
- Enzymes for protein synthesis are on the ribosomes.
Cells may be specialized to carry out a particular function.
Cell Specialization
Now we have established the general
features of both animal and plant cells we must also remember that many
cells do look different and this is because they have their own
special jobs to do. These cells display specialized features that make
them suited to carry out their specific function.
Cell Specialization – Animals
| Cell Type | Specific Function | Specialised Feature |
| Red Blood Cell | ||
 |
Contain haemoglobin which transports oxygen to other cells and around the body. |
|
| Sperm Cell | ||
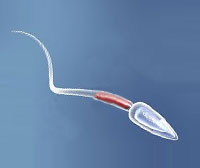 |
To fertilise the ovum (female egg cell). |
|
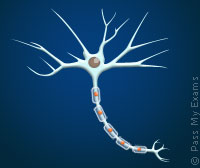
| Nerve Cell | ||
 [Motor Nerve Cell] |
Transmit electrical nerve impulses and so carry information from one part of the body to another ie from receptor to an effector. |
|
Cell Specialisation – Plants
| Cell Type | Specific Function | Specialised Feature |
| Xylem Cell | ||
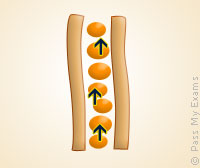 |
Small tubes that carry water from the roots to the leaves. |
|
| Root Hair Cell | ||
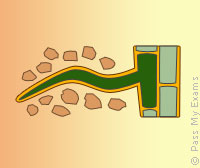 |
Absorb water and mineral ions from the soil. |
|
| Leaf Palisade Cell | ||
 |
Carries out photosynthesis. |
|
Tissues, organs and systems
- A tissue is a group of similar cells carrying out a particular function.
- An organ is a group of different tissues carrying out a particular function.
- A system is a group of different organs carrying out a particular function.




No comments:
Post a Comment